ThreadLocal与FastThreadLocal
概要
ThreadLocal 用于提供线程局部变量,在多线程环境可以保证各个线程里的变量独立于其它线程里的变量。也就是说 ThreadLocal 可以为每个线程创建一个【单独的变量副本】,相当于线程的 private static 类型变量
ThreadLocal 的作用和同步机制有些相反:同步机制是为了保证多线程环境下数据的一致性;而 ThreadLocal 是保证了多线程环境下数据的独立性
ThreadLocal源码分析
set(T value)和get()方法
set(T value) 方法中,首先获取当前线程,然后在获取到当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap,如果 ThreadLocalMap 不为 null,则将 value 保存到 ThreadLocalMap 中,并用当前 ThreadLocal 作为 key;否则创建一个 ThreadLocalMap 并给到当前线程,然后保存 value。
ThreadLocalMap 相当于一个 HashMap,是真正保存值的地方。
1 | |
在 get() 方法中也会获取到当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap,如果 ThreadLocalMap 不为 null,则把获取 key 为当前 ThreadLocal 的值;否则调用 setInitialValue() 方法返回初始值(null),并保存到新创建的 ThreadLocalMap 中。
1 | |
setInitialValue() 是 ThreadLocal 的初始值,默认返回 null,子类可以重写改方法,用于设置 ThreadLocal 的初始值:
1 | |
remove()
remove()用来移除当前 ThreadLocal 对应的值。同样也是同过当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 来移除相应的值。
1 | |
当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap(getMap(t))
在 set,get,initialValue 和 remove 方法中都会获取到当前线程,然后通过当前线程获取到 ThreadLocalMap,如果 ThreadLocalMap 为 null,则会创建一个 ThreadLocalMap,并给到当前线程。
1 | |
每一个线程都会持有有一个 ThreadLocalMap,用来维护线程本地的值,在Thread类中:`
1 | |
在使用 ThreadLocal 类型变量进行相关操作时,都会通过当前线程获取到 ThreadLocalMap 来完成操作。每个线程的 ThreadLocalMap 是属于线程自己的,ThreadLocalMap
中维护的值也是属于线程自己的。这就保证了 ThreadLocal(类型为ThreadLocalMap)变量在每个线程中是独立的,在多线程环境下不会相互影响。
ThreadLocalMap
构造方法
ThreadLocal 中当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 为 null 时会使用 ThreadLocalMap 的构造方法新建一个 ThreadLocalMap:
1 | |
构造方法中会新建一个数组,并将将第一次需要保存的键值存储到一个数组中,完成一些初始化工作。
存储结构
ThreadLocalMap 内部维护了一个哈希表(数组)来存储数据,并且定义了加载因子:
1 | |
table 是一个 Entry 类型的数组,Entry 是 ThreadLocalMap 的一个内部类:
1 | |
保存键值对
调用ThreadLocalMap的set(ThreadLocal key, Object value)方法将数据保存到哈希表中:
1 | |
首先使用 key(当前 ThreadLocal)的 threadLocalHashCode 来计算要存储的索引位置 i。threadLocalHashCode 的值由 ThreadLocal 类管理,每创建一个 ThreadLocal 对象都会自动生成一个相应的 threadLocalHashCode 值,其实现如下:
1 | |
在保存数据时,如果索引位置有 Entry,且该 Entry 的 key 为 null,那么就会执行清除无效 Entry 的操作,因为 Entry 的 key 使用的是弱引用的方式,key 如果被回收(即 key 为 null),这时就无法再访问到 key 对应的 value,需要把这样的无效 Entry 清除掉来腾出空间。
在调整 table 容量时,也会先清除无效对象,然后再根据需要扩容。
1 | |
获取Entry
取值是直接获取到 Entry 对象,使用 getEntry(ThreadLocal key) 方法:
1 | |
因为可能存在哈希冲突,key 对应的 Entry 的存储位置可能不在通过 key 计算出的索引位置上,也就是说索引位置上的 Entry 不一定是 key 对应的 Entry。所以需要调用 getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) 方法获取。
1 | |
移除Entry
1 | |
内存泄露原因分析
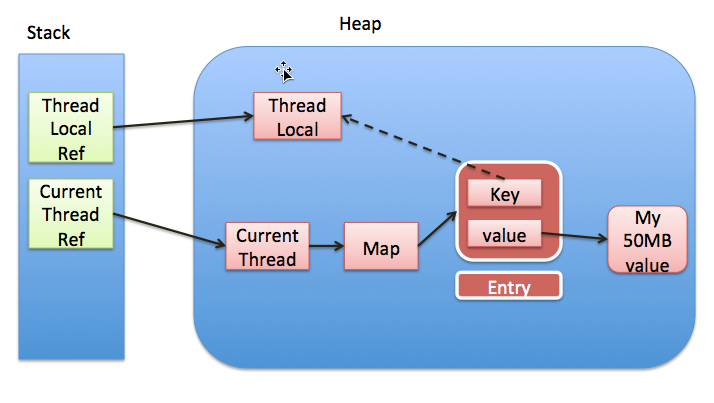
ThreadLocal的实现是这样的:每个Thread 维护一个 ThreadLocalMap 映射表,这个映射表的 key 是 ThreadLocal实例本身,value 是真正需要存储的 Object。
也就是说 ThreadLocal 本身并不存储值,它只是作为一个 key 来让线程从 ThreadLocalMap 获取 value。值得注意的是图中的虚线,表示 ThreadLocalMap 是使用 ThreadLocal 的弱引用作为 Key 的,弱引用的对象在 GC 时会被回收。
为何会内存泄露
从上图可以看出,ThreadLocal对象是被两种引用指向的:
- 强引用: 对应的
ThreadLocalRef, 也就是我们代码中显示声明的ThreadLocal对象 - 弱引用: 对应的是
ThreadLocalMap中的Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>>,作为 key 以一个弱引用指向ThreadLocal对象。
当强引用断开的时候,此时ThreadLocal对象只有一个弱引用指向了,那么GC发生时,ThreadLocal对象就会被回收。但此时 key==null, value已经不能被应用程序访问到了,当前线程如果没有被回收的情况下(如线程池),仍有一个引用链Thread Ref -> Thread -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value存在,成了脏数据,造成了内存泄漏
ThreadLocalMap的设计
ThreadLocalMap的设计中已经考虑到这种情况,也加上了一些防护措施:在ThreadLocal的get(),set(),remove()的时候都会清除线程ThreadLocalMap里所有key为null的value,并清理对应的 Entry。
但是这些被动的预防措施并不能保证不会内存泄漏:
- 使用static的ThreadLocal,延长了ThreadLocal的生命周期,可能导致的内存泄漏
- 分配使用了ThreadLocal又不再调用get(),set(),remove()方法,那么就会导致内存泄漏。
为什么使用弱引用
先来看看官方文档的说法:
To help deal with very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use WeakReferences for keys.
为了应对非常大和长时间的用途,哈希表使用弱引用的 key。
下面我们分两种情况讨论:
- key 使用强引用:引用的ThreadLocal的对象被回收了,但是ThreadLocalMap还持有ThreadLocal的强引用,如果没有手动删除,ThreadLocal不会被回收,导致Entry内存泄漏。
- key 使用弱引用:引用的ThreadLocal的对象被回收了,由于ThreadLocalMap持有ThreadLocal的弱引用,即使没有手动删除,ThreadLocal也会被回收。value在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set,get,remove的时候会被清除。
比较两种情况,我们可以发现:由于ThreadLocalMap的生命周期跟Thread一样长,如果都没有手动删除对应key,都会导致内存泄漏,但是使用弱引用可以多一层保障:弱引用ThreadLocal不会内存泄漏,对应的value在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set,get,remove的时候会被清除。
因此,ThreadLocal内存泄漏的根源是:由于ThreadLocalMap的生命周期跟Thread一样长,如果没有手动删除对应key就会导致内存泄漏,而不是因为弱引用。
使用ThreadLocal
- 使用ThreadLocal,建议用static修饰 static ThreadLocal
headerLocal = new ThreadLocal(); - 使用完ThreadLocal后,执行remove操作,避免出现内存溢出情况。
在使用线程池的情况下,没有及时清理ThreadLocal,不仅是内存泄漏的问题,更严重的是可能导致业务逻辑出现问题。所以,使用ThreadLocal就跟加锁完要解锁一样,用完就清理。
FastThreadLocal
Netty 中使用 FastThreadLocal 作为 ThreadLocal 的扩展, ThreadLocalMap 中使用线性探测的方式解决hash冲突的问题,如果没有找到空闲的slot,就不断往后尝试,直到找到一个空闲的位置,插入entry,这种方式在经常遇到hash冲突时,影响效率。
FastThreadLocal 直接使用数组避免了hash冲突的发生,对每一个FastThreadLocal实例创建时,分配一个下标index;分配index使用AtomicInteger实现,每个FastThreadLocal都能获取到一个不重复的下标
FTL 关键类
FastThreadLocal 使用了 FastThreadLocalThread 和 InternalThreadLocalMap 两个类
FastThreadLocalThread是对Thread类的一层包装,每个线程对应一个InternalThreadLocalMap实例
1 | |
InternalThreadLocalMap 主要由两个成员组成(继承于 UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap),其中 indexedVariables 作为一个 Object[]数组,直接用来存放 FastThreadLocal 对应的 value,每个 FastThreadLocal 对象都会在相应的线程的 ThreadLocalMap 中被分配到对应的 index,而这里的具体下标,则由以上的 nextIndex 成员在每个 FastThreadLocal 初始化的时候分配:
1 | |
FTL get 和 set 过程
get 操作比较简单, 就是先获取 InternalThreadLocalMap, 这里分为 fastGet 和 slowGet:
- fastGet: 如果当前Thread是 FastThreadLocalThread, 则直接获取
InternalThreadLocalMap, 然后根据 FTL 的下标获取对应值 - slowGet: 当前 Thread 是普通 Thread, 则通过 ThreadLocal 包一下
InternalThreadLocalMap返回, 然后根据 FTL 下标获取值1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42// FastThreadLocal.get
public final V get() {
return get(InternalThreadLocalMap.get());
}
public final V get(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return (V) v;
}
return initialize(threadLocalMap);
}
// InternalThreadLocalMap.get
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
return slowGet();
}
}
// InternalThreadLocalMap.fastGet
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
// InternalThreadLocalMap.slowGet
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap.slowThreadLocalMap;
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
1 | |
set 操作
1 | |
FTL 对比 ThreadLocal 快在哪
- FastThreadLocal 在具体的定位的过程中,只需要根据在构造方法里获取得到的具体下标就可以定位到具体的数组位置进行变量的存取,而在 jdk 原生的 ThreadLocal 中,具体位置的下标获取不仅需要计算 ThreadLocal 的 hash 值,并需要在 hashTable 上根据 key 定位的结果,一旦定位之后的结果上已经存在其他 ThreadLocal 的变量,那么则是通过线性探测法,在 hashTable 上寻找下一个位置进行,相比 FastThreadLocal 定位的过程要复杂的多。
- FastThreadLocal 由于采取数组的方式,当面对扩容的时候,只需要将原数组中的内容复制过去,并用 NULL 对象填满剩余位置即可,而在 ThreadLocal 中,由于 hashTable 的缘故,在扩容后还需要进行一轮 rehash,在这过程中,仍旧存在 hash 冲突的可能。
- 在 FastThreadLocal 中,遍历当前线程的所有本地变量,只需要将数组首位的集合即可,不需要遍历数组上的每一个位置。
- 在原生的 ThreadLocal 中,由于可能存在 ThreadLocal 被回收,但是当前线程仍旧存活的情况导致 ThreadLocal 对应的本地变量内存泄漏的问题,因此在 ThreadLocal 的每次操作后,都会进行启发式的内存泄漏检测,防止这样的问题产生,但也在每次操作后花费了额外的开销。而在 FastThreadLocal 的场景下,由于数组首位的 FastThreadLocal 集合中保持着所有 FastThreadLocal 对象的引用,因此当外部的 FastThreadLocal 的引用被置为 null,该 FastThreadLocal 对象仍旧保持着这个集合的引用,不会被回收掉,只需要在线程当前业务操作后,手动调用 FastThreadLocal 的 removeAll()方法,将会遍历数组首位集合,回收掉所有 FastThreadLocal 的变量,避免内存泄漏的产生,也减少了原生 ThreadLocal 的启发式检测开销。